Big Blue Big Blue is the name employed since the 1980s by IBM. International Business Machines Corporation (IBM). The name may have sprung from the blue hue of the early displays on computers or the dark blue hue of its corporate logo. Big Blue arose in the early 1980s , in the financial and popular press as a name for IBM. The name isn’t clear as to its origins, but is believed to be referring to the blue hue of the cases on IBM’s computers.1
The name was adopted by IBM which is content to leave its roots in the shadows and has named a number of its projects with a nod to the origins to the name. For instance, Deep Blue, IBM’s computer for chess, was took on and eventually defeated the world’s top player Garry Kasparov in a controversial tournament in 1997. The first printed mention of Big Blue Big Blue nickname appeared in the June 8th, 1981 publication of Businessweek magazine. The magazine is believed to be the work of an unidentified IBM fan.
The computing industry has the kind of commitment to its customers that IBM has, and the company has done this by providing its legendary customer support and service … In result, it’s not unusual to see customers refusing to purchase any equipment that isn’t manufactured by IBM even though it’s more affordable. I don’t want to think that I shouldn’t have stayed with IBM’s Big Blue
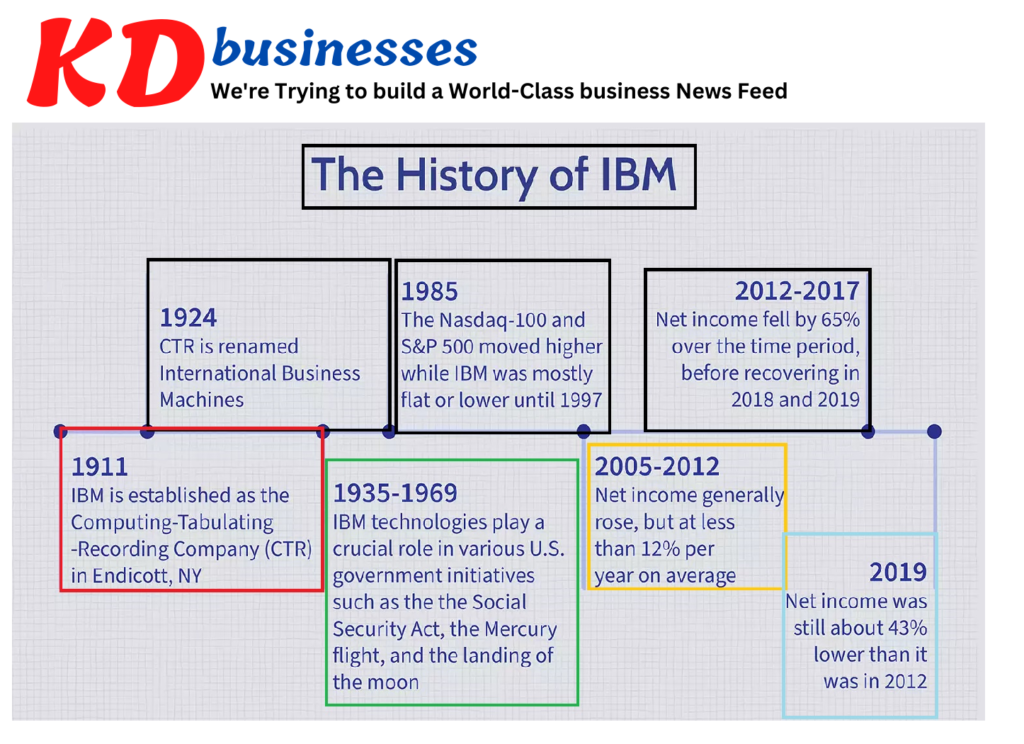
IBM began in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR) in Endicott, NY. CTR was an holding corporation established in 1912 by Charles R. Flint that combined three companies which manufactured scales, punch-card information processors and employee time clocks and even meat slicers. The year 1924 saw the first time that CTR became known as International Business Machines.
In the subsequent century IBM was to be one of world’s leading technological innovators, creating the technology, inventing it, and creating hundreds of software and hardware information technology. IBM is the source of many inventions that soon became standard such as for instance the Barcode UPC as well as the magnetic stripe card personal computer and the floppy disk the drive for hard disks and the ATM. ATM.
IBM technologies were essential to the success in U.S. government initiatives such as the introduction of the Social Security Act in 1935. They also played a role in many NASA missions starting with 1964’s Mercury flight until that 1969 lunar landing, and even beyond. IBM has the largest number of U.S. patents of any firm and, as of today, IBM employees have been recognized with a variety of prestigious titles including five Nobel Prizes as well as the six Turing Awards. The first multi-national group companies to be established within U.S. history, IBM is a global company that spans 175 countries around the world and employing 350,000 people worldwide.
Exemples of the Financial Success of Big Blue
IBM has been underperforming the larger S&P 500 index and Nasdaq-100 index. The major divergence started in 1985 , when the Nasdaq-100 as well as the S&P 500 moved higher while IBM was generally in the middle or at a lower level until 1997. Since then, it has been losing ground in comparison with the index of Nasdaq 100.
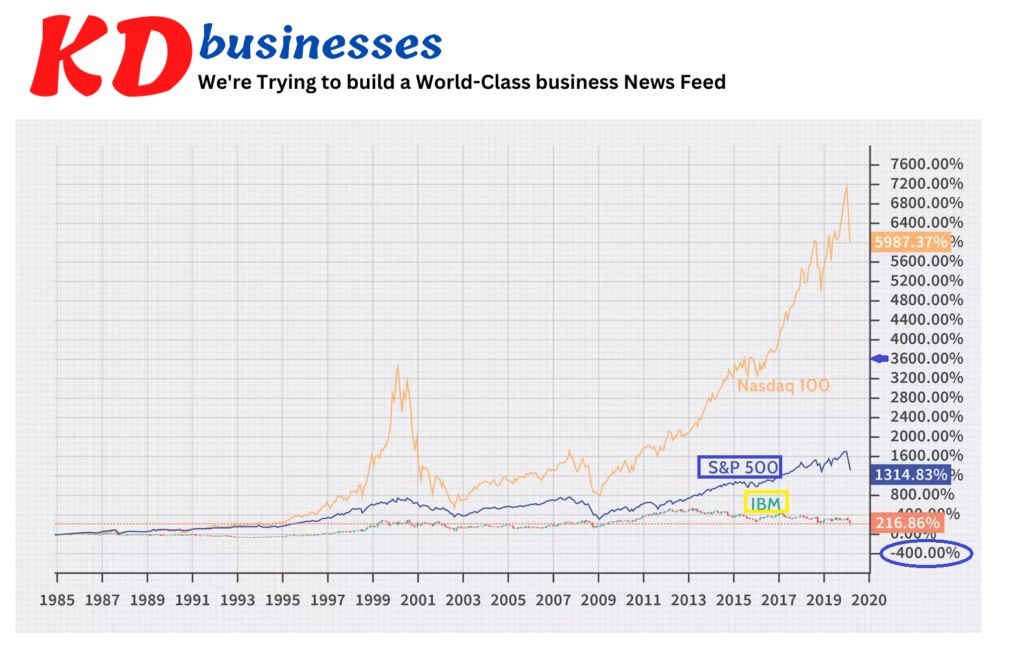
The decline in the share prices between 1985 and the year 2019 illustrated by the company’s financial performance. From 2005 to 2012 the net profit generally increased, but with less than 11% in average. In the years between 2012 and 2017 net income dropped by 65% during the course of time, only to begin rebounding in 2018 and the year 2019. In 2019, however net income was just 43% less than in 2012.